Important Questions & Answers: Demographic Structure & Indian Society - 2 | Sociology Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
It is right that the population explosion is responsible for our lower standard of living. The population has been increased but per capita income has not been increased rather it has been reduced. If the population increases but national income does not increase, then, the growth rate will come down. Lower per capita income will lead to less consumption which results in a lower standard of living. It also leads to a bad impact on the health and working efficiency of the person.
Q.32. How increasing population could be controlled? Give two ways.
- Agricultural production of the country should be increased and industries should be developed so that the per capita income and national income could be increased. It will lead to a higher standard of living and low birth rate.
- Education is necessary for a higher standard of living so that people should remain conscious about the merits of less number of children: It will result in a reduction of population growth.
Q.33. What are the demerits of more population?
- It will lead to an increase in problems like poverty, unemployment, etc.
- The living standard of the people remains lower.
- The health of the people deteriorates with this.
- The problem of food affects the whole country.
- Economic development, national income and per capita income reduce with this.
Q.34. What was the population of India in 1951 and 2001?
In 1951, the Indian population was 36.11 crore out of which 29.9 crore people lived in rural areas and 6.2 crore people lived in urban areas. In 2001, the Indian population was 102.70 crore out of which 74.2 crores were in rural areas and 28.5 crore people were in urban areas.
Q.35. What is Family Planning?
Family planning means to keep the small size of the family so that the income of the family should remain higher than expenditure. If income will be higher than expenditure then it will lead to a higher standard of living.
Q.36. To which religion do people of India belong?
People in India belong to different religions. 79.5% people are Hindus, 13.2% are Muslims, 2.4% are Christians, 2.1% are Sikhs, 0.81% are Buddhists, 0.5% are Jains and 0.5% belong to Parsi and other tribal religions.
Q.37. Tell something about Sex Ratio in IndiJi.
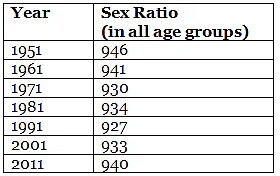
Sex ratio is a cause of concern in India which) is reducing day by day. People want to have a male child and that is why they kill girl child even before birth. Thus, the number of females is decreasing. Only two states in India are there where females are more in number than males. Everything will be clear by the given data.
Q.38. Show and explain the distribution of sex ratio in India on the outline political map of India.
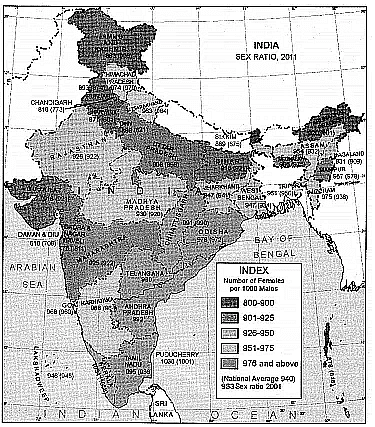
This map tells us that many states like Kerala, A.P. and others have sex ratio more than 1000: 950 but some states like Punjab and Haryana have around 1000: 880 of sex ratio. The map also shows that great inequality exists in our India regarding sex ratio.
Q.39. How can you say that village is a social unit?
It is right that a village is a social unit. If we study Indian villages carefully then we would come to know that village is the main base of Indian culture. More than 70% of Indian population lives in villages and they are engaged in agricultural work, yet a number of changes are coming in villages but still, it is active in the form of a unit. Rural society is the main base of the Indian social structure. People of villages live in harmony with each other and celebrate their festivals with each other. They have primary and personal relations. In this way, we can say that village is a social unit.
Q.40. What are the changes coming in the rural community?
- Now more and more people from villages are running towards cities.
- Now villagers are getting more education.
- Modern means of agriculture are being used these days.
- The caste system has lost its importance and the class system is taking its place.
- Now the social status of a person is determined by his individual traits.
- Formal relations are increasing instead of informal relations.
Q.41. Explain regional variations of low child sex ratio in India.
- Lowest child sex ratios are found in the most prosperous regions of India.
- Punjab, Haryana, Chandigarh, etc. are among the richest states in India in terms of per capita income, they also are the states with the lowest child sex ratio.
- The problem of selective abortions is not due to poverty, dowry or lack of resources but is due to wish to have a male child.
- Economically prosperous families decide to have fewer children. They may choose the sex of their child.
Q.42. The family programme suffered during the period of National emergency. Give reasons.
- Introduction of a coercive programme of mass sterilization.
- the Vast number of mostly poor and powerless people were forcibly sterilized.
- Sterilisation refers to medical procedures like vasectomy for men and tubectomy for women which prevent conception and childbirth.
- There was massive pressure on lower-level government officials (school teachers or office workers) to bring people for sterilization in the camps; that was organized specially for this purpose.
- Widespread popular opposition to the programme.
Q.43. Why is it necessary to reduce the birth rate in India?
- More birth rate can lead to the danger of population explosion.
- More birth rate can lead to a reduction in per capita income and national income.
- More birth rate can lead to the problem of the food supply.
- It will increase the problems of poverty and unemployment.
- It will lead to the need for more investment.
Q.44. Give the main features of the National Population Policy 2000.
- To reduce the infant mortality rate to 30 per 1000.
- To reduce the maternal mortality rate to 100 per lakh.
- To encourage the late marriage of girls.
- Complete registration of birth, death and marriage.
- To take steps to give compulsory and free education to the children till the age of 14 years.
- To stop the spread of aids.
- To encourage family planning programme.
Q.45. Why is population control necessary?
- It leads to an increase in per capita income.
- It increases the savings and growth of capital formation.
- It leads to a higher standard of living.
- We can find the solution to many problems like poverty, unemployment, etc.
- It reduces the prices of commodities and the problem of food also get solved with this.
- It can lead to more expenditure on public welfare.
Q.46. How population affects economic development?
If the population will be more then it will have an adverse impact on economic development because if consumption will be more then production and the resources of the country will be depleted very quickly. It will reduce the national income and country will become poor. If the population will be less, then it will have a very good impact on economic development because production will be more than consumption. Resources of the country will remain intact for a longer period of time. Per capita income and national income of the country will increase as well. The living standard will remain high. In this way, less or more population have a great impact on the economic development of the country.
Q.47. What are the merits of less population?
- The living standard of the people remains high.
- Health condition of the people remains good.
- Everyone gets employment.
- Employment leads to a reduction in poverty.
- Needs of everyone are fulfilled with this.
Q.48. What is Migration? How many types of migration are there?
Migration is an English which is to move towards other places by leaving one’s basic place of living. So, when a person leaves his place of birth and starts living at another place, then it is known as migration. He can come back to his basic place of living. It is of four types. First one is daily migration in which people go to other places for work, education or occupation in the morning and come back to their native place in the evening. The second one is seasonal migration in which people move towards another place in a specific season and come back to their native place at the end of the season.
For example, migration of labour at the time of harvesting of agricultural produce. The third one is occasional migration in which a person has to migrate if any specific circumstance arises due to any disease or any other reasons. Fourth and last one is permanent migration in which a person leaves his native village, city or country and migrates towards other city or country.
Q.49. Which 22 languages are given in the Constitution of India?
- Manipuri
- Nepali
- Sindhi
- Sanskrit
- Bangla
- Telugu
- Gujarati
- Kannada
- Odiya
- Assamese
- Urdu
- Kashmiri
- Tamil
- Punjabi
- Marathi
- Malayalam
- Hindi
- Konkani
- Dogri
- Santhali
- Maithili
- Bodo.
Q.50. Which two checks of population control are given by Malthus?
- Positive Checks: Those checks which are implemented by nature are called positive checks. That’s why the death rate increases. For example, war, epidemic, earthquake, famine, tsunami, flood, etc. These natural checks are very painful but they reduce the population to a great extent. These checks are not permanent.
- Preventive Checks: These types of checks are the efforts made by humans. These are divided into two parts-morality and prevention through artificial means, sin moral checks, a person uses his mental level to control the population. In artificial means, Malthus tells about those means which are related by humans to control the population. According to Malthus, moral checks are good but artificial checks are against religion.
Q.51. Why the programme of Family Planning was not very successful in India?
- People lack the proper means of family control. Whatever means are available with them, they are not properly used as well. That is the reason why this programme hardly became a success.
- Literacy level in India is quite low due to which they are unable to understand the merits of a small family. They are hardly aware of the fact that more number of children will affect the income of the family.
- Family planning programme is being run by the government and it always lacks financial resources. The given amount was always not enough for the whole of the country.
Q.52. According to Ogburn and Nimkoff, how villages were developed?
- According to them, humans lived in jungles in the first stage. They were hunting animals or were collecting things to eat. They used to move to that place where food was available. Development of villages was not possible at this stage.
- In the second stage, humans started to rear animals instead of killing them. Animals need fodder to eat. That is why people started to settle at those places where it was available. They used to leave the place when fodders depleted. That is the reasons why villages were also not developed at that stage.
- In the third stage, a man came to know about the growing of plants. When they came to know about the growth of plants then they started to live in one place. Since food was available, they started to live a settled life. In this way, the villages came in front of us.
Q.53. Why is Urbanization increasing?
- The country is becoming more industrialized.
- More facilities are there in urban areas.
- Services like education, medical facilities, etc. are easily available in cities.
- Employment is easily available in cities.
- More security is there in cities.
Q.54. Why are the village Panchayats necessary for villages?
India is basically an agricultural country where more than 70% population is engaged in agricultural works. Powers are decentralized by the Indian government so that villages could be developed and the administration of villages should run smoothly. Every¬one the orders of Panchs in villages. These days Panchayats even have the right to collect tax and to maintain peace in villages. That is why the village Panchayat is necessary.
Q.55. In what way formal demography is different from social demography?
- Focus on social, economic and political aspects.
- Enquires into causes and consequences of population structures and changes.
- Social processes and structures regulate demographic processes.
- Trace the social resources for population trends.
Q.56. “Literacy as a prerequisite to education is an instrument of empowerment.” Discuss.
- It can lead to health awareness and fuller participation in the cultural and economic well-being of the community.
- Literacy varies considerably across gender.
- It is still very low in social groups.
- Inequalities in literacy tend to reproduce inequality across generations.
- Regional variations are still very wide.
The document Important Questions & Answers: Demographic Structure & Indian Society - 2 | Sociology Class 12 - Humanities/Arts is a part of the Humanities/Arts Course Sociology Class 12.



